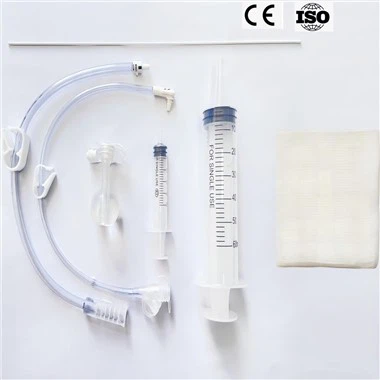
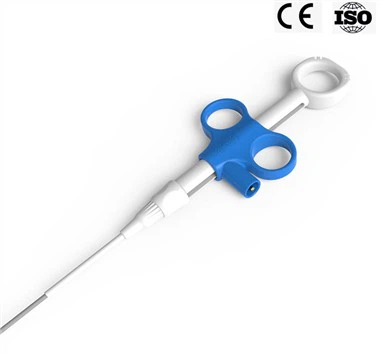
Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS) Needle

The multi-section design of the needle tip draws on the application of the golden section law in mechanical strength.
The large-angle design of the front end enables the needle tip of more bearing capacity, which can be punctured multiple times without deformation.
Double twist-lock safety device on the handle scale avoids unnecessary needle sticking out, helps physicians accurately grasp the length of the needle at the end of the needle tip during clinical operations, and prevent medical accidents such as puncture.
The probe wire is made of nickel-titanium material, which makes the operation smoother and more flexible.
The point array echo design effectively improves the accuracy of ultrasound imaging and puncture.
Quick lock needle adjuster ensures safe operation of the entire biopsy process.
The lockable syringe is easy to operate, and the aspiration process is simple and precise.
Products Description
|
Code |
Needle outer diameter (mm) |
Maximum extension length of needle (mm) |
Maximum working length of needle (mm) |
Sheath outer diameter (mm) |
Applicable endoscope channel (mm) |
|
UN18-19/140 |
1.1mm |
80mm |
1415mm |
1.7mm |
≥2.0mm |
|
UN18-20/140 |
0.90mm |
80mm |
1415mm |
1.7mm |
≥2.0mm |
|
UN18-22/140 |
0.70mm |
80mm |
1415mm |
1.7mm |
≥2.0mm |
|
UN18-25/140 |
0.50mm |
80mm |
1415mm |
1.7mm |
≥2.0mm |
|
UN18-19/70 |
1.1mm |
80mm |
715mm |
1.7mm |
≥2.0mm |
|
UN18-20/70 |
0.90mm |
80mm |
715mm |
1.7mm |
≥2.0mm |
|
UN18-22/70 |
0.70mm |
80mm |
715mm |
1.7mm |
≥2.0mm |
|
UN18-25/70 |
0.50mm |
80mm |
715mm |
1.7mm |
≥2.0mm |

Since its initial report by Henriksen et al[1], endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration (EUS-FNA) has now been incorporated into the diagnostic and staging algorithm for the evaluation of benign and malignant diseases of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract and of adjacent organs[2]. Its introduction constitutes a major breakthrough in the endoscopic field and has gradually transformed EUS from a pure imaging modality into a more interventional and lately therapeutic procedure. In addition, the possibility of collecting samples, providing a definitive cytological and/or histological evidence of the presence of malignancy, has strongly contributed to changing EUS from a subjective, highly operator dependant procedure into a more objective one.
In this article, we have done a critical appraisal of recent published literature and reviewed the instrumentation, technique and the most important clinical applications of EUS-FNA. The role of EUS in diagnosis and staging of esophageal, gastric, rectal cancers, subepithelial tumors, pancreatobiliary cancers, mediastinal cancers, lung and miscellaneous tumors has been dealt with. Despite the availability of advanced cross sectional imaging like computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging, EUS is still the gold standard for diagnosis and staging of various gastrointestinal cancers in particular of the pancreas, due to its high sensitivity and specificity and safe technique of acquiring tissue. We have not covered topics like general role of EUS in diagnosis of pancreatobiliary stone disease, chronic pancreatitis, autoimmune pancreatitis or in screening patients with a family history. We have also not dealt with the most challenging and exciting therapeutic aspect of EUS in stone disease, pseudocysts, celiac blocks and fine needle injection of tumors. We have tried to focus on the issues that have strongest evidence currently and also just mention the controversial topics like use of EUS post neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
Hot Tags: endoscopic ultrasound (eus) needle, China endoscopic ultrasound (eus) needle manufacturers, suppliers, EUS, Endoscopic Ultrasound Fine Needle Puncture, Endoscopic Ultrasound Needle, Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS) Needle
Previous
No InformationYou Might Also Like
Send Inquiry